If you have finished a high-density exercise and feel that the heart rate and breathing are high for a while, I have suffered from EPOC- Effect after burns. Short Oxygen consumption after excess exerciseEPOC refers to Increase the rate of intake of the oxygen that your body uses after exercise to restore itself to its condition before the exercise.
But EPOC is more than just a post -exercise phenomenon. It plays an important role in Calorie expensesEspecially in certain types of training, such as Welcome Resistance exercises. In this article, we will explore what Epoc is, how it works, and why it matters, and how to train in ways to increase its benefits.
What is EPOC (surplus oxygen consumption)?
Epoc is the amount The additional oxygen that your body consumes after an intense practice To provide the recovery process. The body shares several operations that take energy during recovery:
- Renewing ATP stores and phosphate brokenness
- Muscle glycogen
- Remove and convert lactate (CORI course)
- Restoring the levels of hemoglobin and myjlobin
- Thermal organization (body cooling down)
- Increased hormone activity (katiculine, cortisol, GH)
- Muscle tissue repair and adaptation
Each of these require oxygen, and contribute to the high metabolism after exercise. Basically, EPOC reflects Additional energy uses your body after exercise To return to balance. During this recovery period, your MetabolismYour body continues to burn calories – even during rest.
You may get to know the post -pregnancy effect if, after exercise:
- Your heart rates and breathing are high
- It continues to sweat or feel heat
- Your device displays the burning of higher calories
- You feel more tired or stimulated after training
These signs reflect your body She is still recoveringAnd you reap the metabolic rewards for a smart and intense session.
It requires high levels of EPOC Very intense or long exerciseWhich may not be possible for most people, especially beginners or non -athletes.
Why is EPOC?
1. It increases the burning of total calories
EPOC expands your power expenses After the exercise periodIt enhances the burning of calories in general. the Severity and duration From your exercise strongly affects the size and length of the EPOC effect.
Studies indicate that EPOC can increase Power expenditures break up to 38 hours After heavy, high -density resistance The session (Mark D. Shunck. And others).
2. Supports fat loss
While the burning calories during exercise are important, the Post -exercise metabolism reinforcement From EPOC it can contribute beneficially to losing fat – especially when combining resistance or heart training.
3. Reinforcement is enhanced
The body uses this dense oxygen to:
- ATP and Phosphocreatine
- Fix the damaged muscles
- Restore hormones such as cortisol and growth hormone
These operations are necessary for Training adaptation and muscle growth.
What affects the EPOC effect?
| factor | Impact on EPOC |
|---|---|
| The severity of the exercise | Supreme density = epoc is larger |
| Exercise period | Long -term = more demand for oxygen |
| Training type | Resistance training and HIit produce EPOC higher than stable heart disease |
| Training experience | Trained individuals may recover faster and test EPOC slightly reduced over time |
Training methods that increase from EPOC to the maximum
1. HIIT
Hiit includes alternating throats from intense voltage with recovery periods. This creates a major metabolic disorder, which requires more energy after exercise to restore physiological balance.
Protocol example:
- 30 seconds enemy / 90 seconds on foot x 8-10 rounds
- Total period: 20-25 minutes
- Density: ≥85 % heart rate as a maximum (or ≥90 % vo₂MAX)
2. Training of the SIT time interval (SIT)
SIT pushes the body above 100 % Vo₂MAX for very short periods, causing more oxygen debt and muscle disruption.
Protocol example:
- 6-8 x 30 seconds “comprehensive” (EG, Cycle Ergometer or Hill Sprints)
- 3-4 minutes of negative recovery between seizures
3. Heavy Resistance Training
Multiple complex elevators using high loads cause a large employment of muscle fiber, ATP, and hormonal response – all of which contributes to EPOC.
Best practices:
- Use Multiple elevators (For example, squatting, Deadlifts, rows, bench Press)
- load: 70-85 % of 1RM
- Quantity: 3-5 sets x 8-12 representatives
- Short rest periods (45-60 seconds) increases metabolism cost
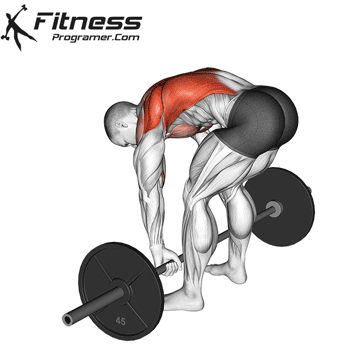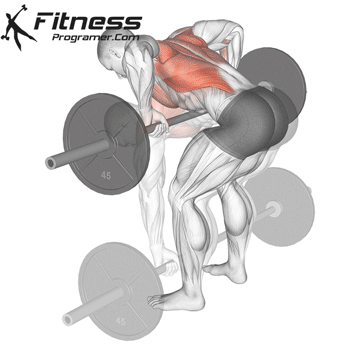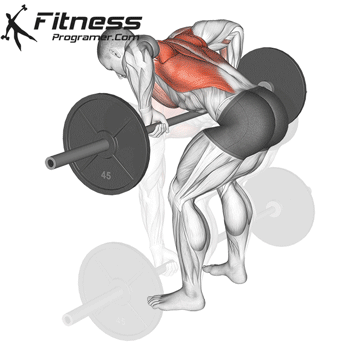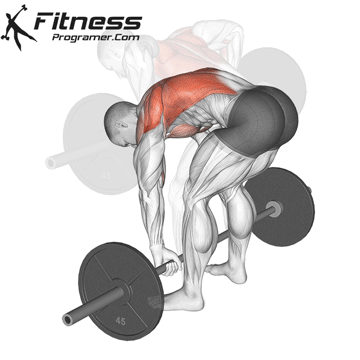
4. Training the department’s resistance
It combines strength and cardiovascular elements with minimal comfort between exercises, and maintaining a high heart rate throughout the session.
Protocol example:
- 4-6 exercises in circle (for example, payment, stab wounds, rows, kettlebell fluctuations)
- 30-60 seconds for each station with rest less than 30 seconds
- Repeat 3-5 rounds
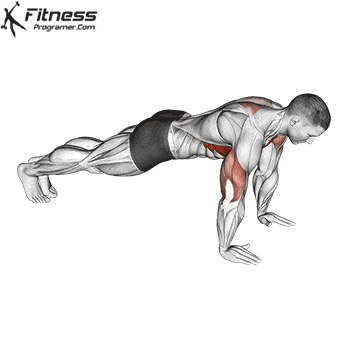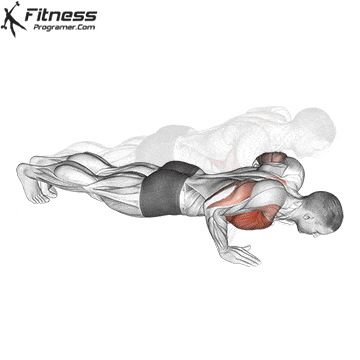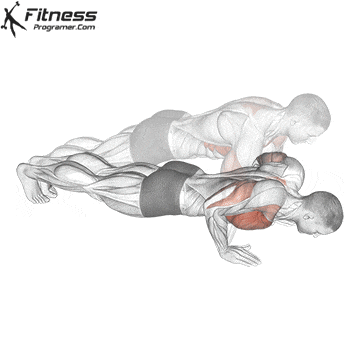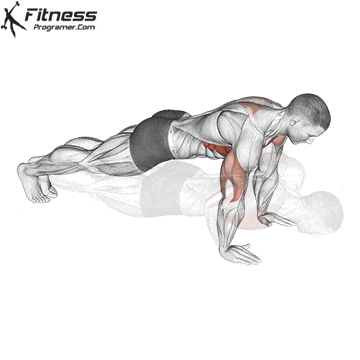
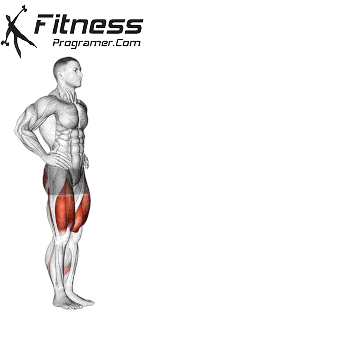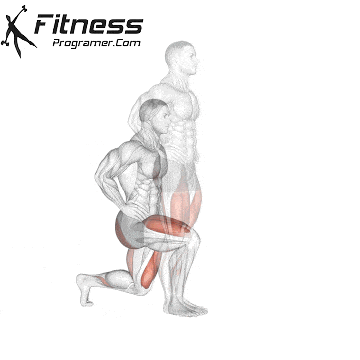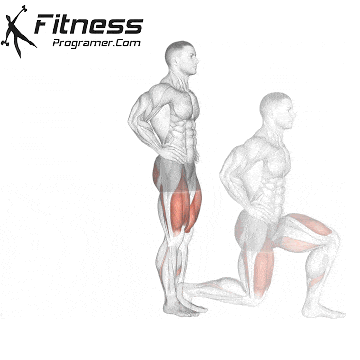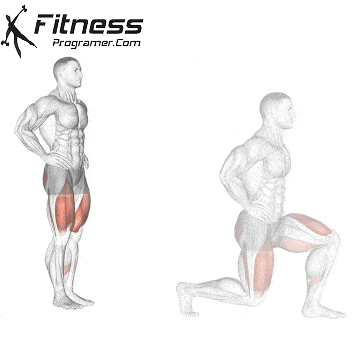
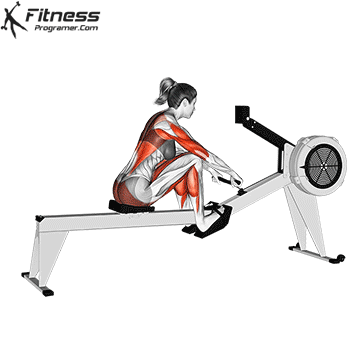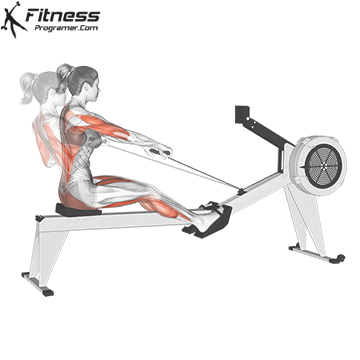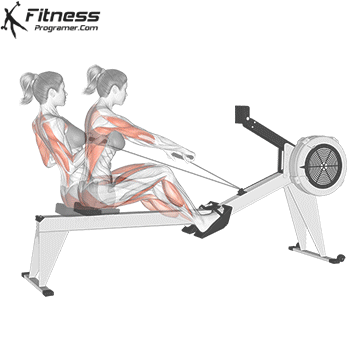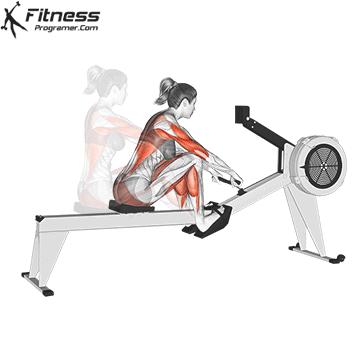
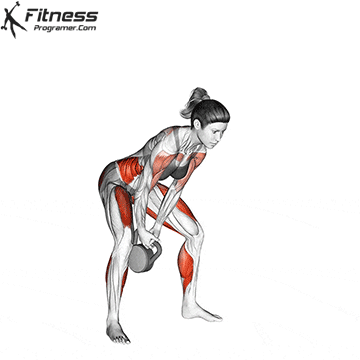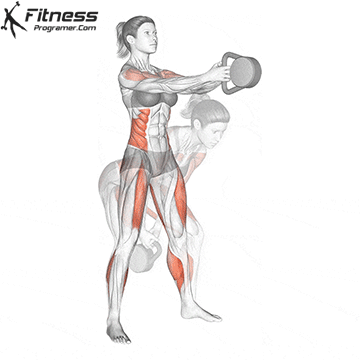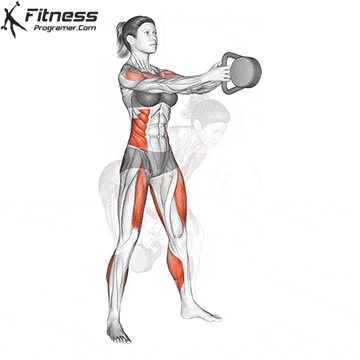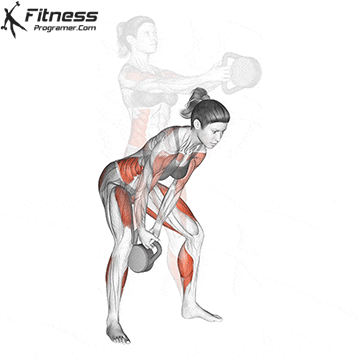
5. Tolerance and joint resistance training (simultaneous training)
Performing air and resistance training in one session increases the cost of total energy and metabolic demand after exercise.
Example session:
- 20 minutes of moderate to the upper resistance
- Following 20 minutes of time breaks or heart in ≥70 % vo₂Max
6. Taba Taba
Of the very intense forms of HIit with very short work rates, Tabata produces a large oxygen deficit in a short time.
Protocol example:
- 8 rounds of 20 seconds, a maximum, 10 seconds, comfort
- Total: 4 minutes for each exercise (for example, squatting squatting, burpees, mountain climbers)
How long does EPOC last?
Recent research indicates:
- Moderate exercise: EPOC may last 1-3 hours
- Under the high Exercise (≥70 % vo₂Max for ≥50 minutes): EPOC may last 3-12 hoursEspecially in trained individuals.
- Superaximal efforts (for example, ≥105 % vo₂Max or high -density time breaks): It can raise metabolism 12-24 hoursAlthough the calories burn are still modest.
- Heavy Resistance Training or Hiit: EPOC may produce up to 16-38 hoursDepending on the volume of training and intensity.
Epoc calorie effect
Even with EPOC long periods, studies show that it is only explained 6-15 % of the total energy cost From exercise.
This is what literature shows:
- Epoc HD
~5-50 kilos of lion/h After exercise
~15-150 kilo calories Depending on the severity and duration - For comparison: Moderate for 45 minutes may burn 400-600 kilos of lionWhile Epoc adds Only 6-15 % (24-90 KW).
Although EPOC does not represent hundreds of additional calories, it can contribute An additional 6-15 % of the total energy cost in your session (Bentsheim & Bahr, 2003).
Common myths about EPOC
| myth | reality |
|---|---|
| EPOC burns hundreds of calories after each exercise | Most EPOC responses range from 50-200 KW calorieDepending on the type of training. |
| Only the heart stimulates EPOC | The resistance training can be born Equal or larger Epoc of the heart. |
| You need to feel exhausted for EPOC | Important intensity, however Smart programming It can provoke EPOC without exhaustion. |
Who benefits more than the training that focuses on EPOC?
- Customers of fat losing Searching for metabolism advantages
- Occupied professionals Looking for short and effective exercises
- Mathematics and tactical population It aims to improve the ability of work and recovery
- Public fitness customers The desire to improve body composition
conclusion
Epoc, or consuming excess oxygen after exercise, is a strong metabolic phenomenon that helps your body Burn calories and recover a long time after the exercise. Through intense training – through resistance training, Hait, or metabolic circles – you can increase this effect to the maximum support Loss of fat, performance and recovery.
Understand EPOC allows you to More smart trainingNot more difficult. Use it as a tool in fitness programming to build more efficient, effective and sustainable results.
Reference
- Shunc, Mark; Mikat, Richard; McBrey, Jeffrey (2002). “The effect of a sharp period of resistance to oxygen consumption after exercise: the effects of body mass management.” The European Journal of Applied Physiology. 86 (5): Bamid 11882927.
- Laforgia J, Withers RT, Gore CJ. The effects of the exercise severity and the duration of oxygen consumption after excess exercise. J Sports Sci. 2006; 24 (12): 1247-1264. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640410600552064
- B botsheim e, bahr r Sports Med. 2003; 33 (14): 1037-1060. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200333140-00002
- Hackney KJ, Engels HJ, Gretebeck RJ. Energy expenses break and delay muscle pain after training in the full body resistance with an eccentric concentration. J Cody Power accuracy. 2008; 22 (5): 1602-1609
- The American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM instructions for testing and describing the exercise, eleventh edition.
https://fitnessprogramer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/What-Is-EPOC-and-Why-It-Matters.jpg
Source link