Bicycle rides, strengthens the lower body, and provides one of the best low -effect exercises available. But frequent movement and long hours in the saddle also affect. From the painful knees to their tense backs, and sometimes more dangerous accidents on the road, injuries are an unfortunate fact for many cycles. The good news is that most cycling injuries can be reduced or managed through smart training, deliberate recovery, and safe passenger habits.
Why are the prevention of injuries to bikers?
Each pedal blow repeats the same movement thousands of times on one trip. Over time, this repetition puts tension on the joints and muscle support. If the situation is parked or lacks strength in the main areas, small problems can add up to quickly. The most common issues include:
- Knee pain Because of the height of inappropriate saddle, poor bike, or weak support muscles around the joint.
- Low rear discomfort From the bad position, long hours in a winning position, or insufficient stability.
- Neck and shoulder strain Facked by tension from carrying the resistance tightly or tending forward.
Cycling also provides a unique risk of incidence compared to other tolerance. Contestants often deal with impact -related injuries, while cyclists face more problems with excessive use and situation. Bicycle risk is a different injury risk from other endurance sports, which means that prevention strategies must be designed according to cycling demands instead of copying them from other training programs.
Another factor is the time in the saddle. Long -distance bikers can ride for hours along, and even entertainment cyclists may spend the entire weekends on the bike. Small palaces can be amplified, such as a slightly improved bracket or a weak shine muscle, over time and increase the possibility of pain.
Ignoring these warning signs can develop chronic conditions. Luxurious patellax syndrome (often called the “knee”), sciatica, and constant neck tight examples are common examples of problems that start small but they rise if left without treatment. Once these problems develop, they can prepare a bicycle for weeks or months, which leads to training and fitness gains.
For many cycles, injuries are not only painful; It intersects training progress and reducing performance capabilities. That is why prevention is more than just a side concentration; It is an essential part of the long -term cycling plan. Staying in good health requires a balance in air conditioning, preparing the right equipment, and vigilance training habits. When these items are in place, bicycle passengers can constantly train, build durability, and spend more time enjoy riding.
Training in the prevention of injuries
The gym is one of the most effective places to build strength and transportation that protects cyclists on the road. The strong foundation reduces corrosion on the joints, improves the position, and makes the body more flexible for unexpected pressure. The main elements of the training plan for preventing injuries include:
- Power Training: Exercises such as squatting, stabs, and hip tendencies strengthening gluten and separation, which occupy the stroke of trauma and protect the knees.
- Basic stability: The panels and dead errors and the main rotating work helps in keeping the position to ride long horses and reduce pressure from the lower back.
- Mobility: The dynamic of the hips, the tendon of the knee, and the shoulders extend to improve elasticity and reduce the chance of excessive use of injuries.
- Training balanceOne brightness exercises and stability ball training enhances control, especially when moving through traffic or in uneven terrain.
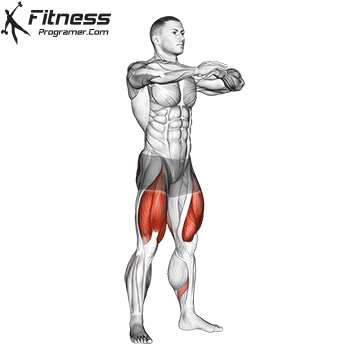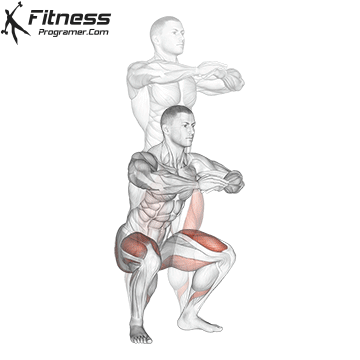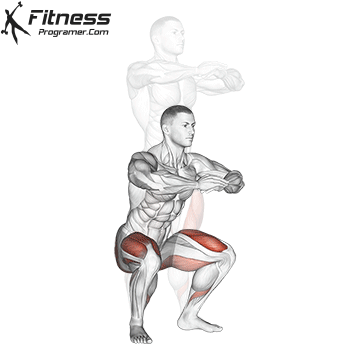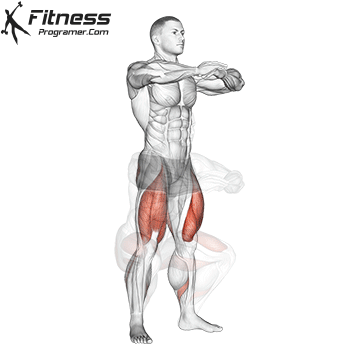
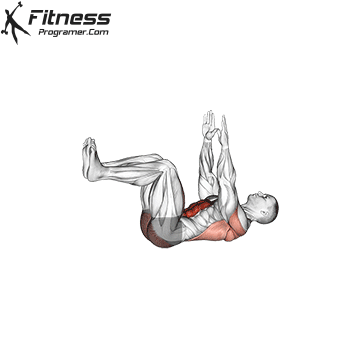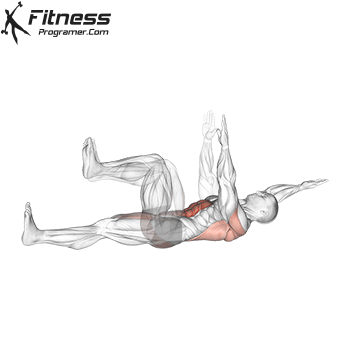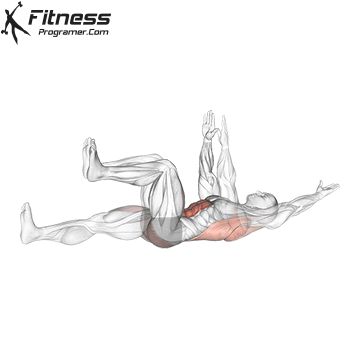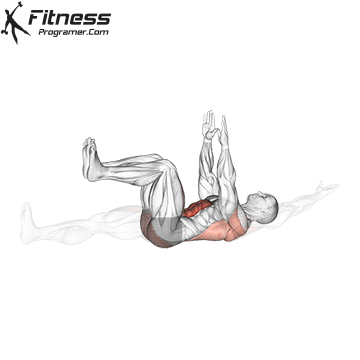
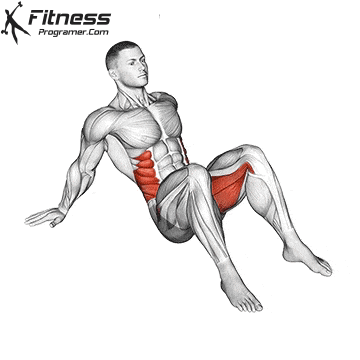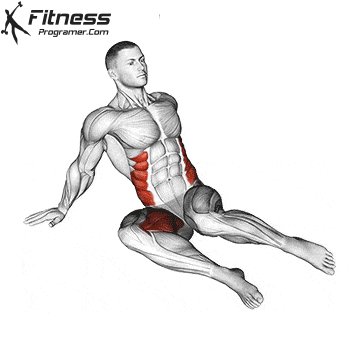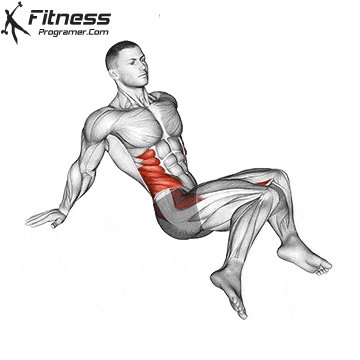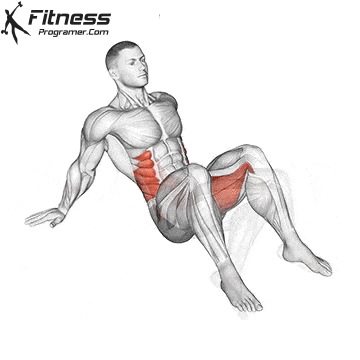
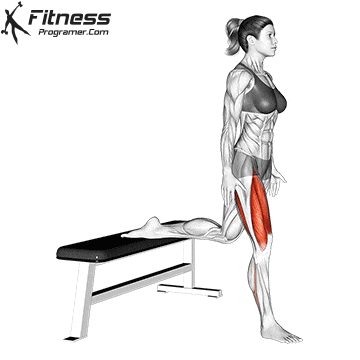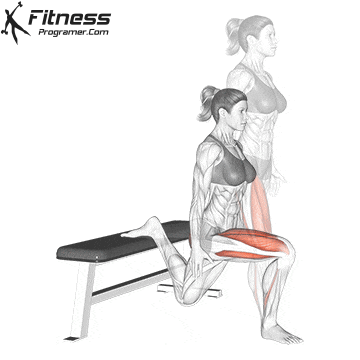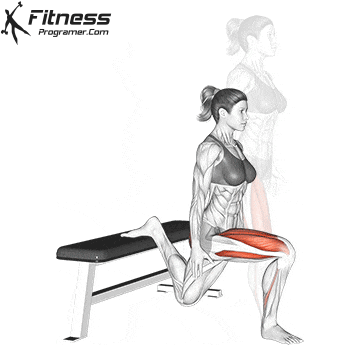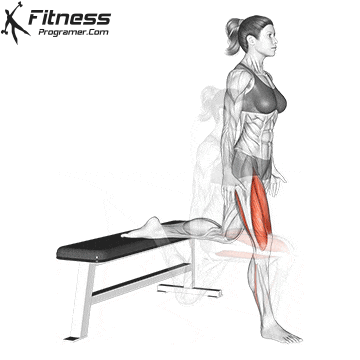
While training can reduce the possibility of excessive injuries, the risks cannot be completely eliminated. Site and horse riding conditions play a major role in the safety of cycling.
For example, Chicago has invested extensively in cycling and cycling infrastructure; However, thick traffic and harsh winter conditions still endanger the risk of accidents compared to cities such as Portland, Oregon, where protected corridors and the most moderate weather create safer conditions. In contrast, heavy car areas such as Houston or Miami often reach higher collision rates due to limited bike infrastructure.
These differences show the impact of the cyclist environment on public safety. In crowded cities such as Chicago, users athletes may well face accidents that cannot prevent training alone. In these cases, consult a Cycling Lawyer in Chicago It can provide valuable support, and help cycles focus on their recovery while ensuring the protection of their rights.
Recovery strategies for cyclists
Recovery is the process that the body adapts to training and returns stronger. Without this, it builds fatigue, low performance, and the risk of infection. The smart recovery plan keeps biking passengers consistent, which are often more important than any one exercise.
1. Active recovery
In days between difficult horseback riding, light activity helps relieve tight muscles and improve blood circulation. Ease of riding a cycling, swimming, or short walking is sufficient to restore movement without adding more pressure.
2. Extending and moving business
Tight hips, knee strings, and shoulders are common complaints among bicycle passengers. The dynamic extends before preparing the body to the movement, while the constant extends after that helps to maintain elasticity. Adding the navigation exercises to the spine and hips also reduces stress on the back during long horse riding.
3. Nutrition and hydration
Suitable fuel speeds up the recovery. Protein supports muscle repair, while carbohydrates renovate the energy executed while riding a bicycle. Stay on the moisture of matters as much, because even moderate dehydration can slow down healing and increase pain. After riding on long or hot horses, adding electrolytes helps replace what is lost through sweat.
4. Comfort and sleep
The recovery strategy does not work without enough comfort. Muscle repair and hormones re -balance during deep sleep, which makes them one of the most effective tools to prevent injuries. The consistency is crucial here, as late nights and irregular sleep can undermine the benefits of even the best training program.
When do you seek professional assistance?
Usually, pain will fade after a day or two, not harmful; However, the pain that declines or gets worse requires attention. Constant discomfort in the knees, back or joints may indicate an injury that requires medical attention. Evidence based resources, such as Basic recovery strategies for young athletes From the American College of Sports Medicine, highlighting when reform procedures are not sufficient and requires professional evaluation.
Long -term cycling safety tips
Preventing excessive use of injuries in training and building a strong recovery routine laying the foundation for consistent performance. However, cyclists also need to consider long -term safety on the road and in their comprehensive customs. A balanced approach in preparation and awareness reduces the risks inside and outside the training.
1. Bike and equipment seizure
Correctly equipped bike is one of the best defenses against chronic pain. Adjusting the height of the saddle and the position of the wheel and the alignment of the link ensures that the body moves efficiently and reduces tension on the joints. Investing in quality equipment, such as the well -carried short pants and well -equipped helmets, also improves comfort and protection.
2. Awareness on the road
Even strong and experienced bike passengers are vulnerable to traffic risks. Stay visible with reflective clothes, using appropriate lighting, and following traffic laws are unsuccessful safety habits. Horse riding expected and avoid deviations, such as headphones, reduces collision chances.
3. Training support
Complementary exercises off the bike, including the basic strength and mobility routine, supports a better position and low risk of infection during long horse riding. For example, merge Leg fluctuations (from front to back) In the warm -up routine, it improves hip movement and the body is considered effective.
4. seasonal considerations
The weather greatly affects the conditions. Wet roads or glaciers require slower speeds and greater caution, while the summer heat increases moisturizing needs. Training and equipment for this season ensures safety while maintaining consistency and effectiveness.
conclusion
Bicycle rides through thousands of frequent movements, which makes prevention of injuries and recovery necessary for long -term performance. Training of strength and mobility in building flexibility, organized recovery procedures prevent fatigue from turning into setbacks, and reducing smart safety habits from risks in training and on the road. By combining these strategies, cyclists can ride with more consistency, confidence and protection against the challenges inherent in this sport.
https://fitnessprogramer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Cycling-Injury-Prevention.webp
Source link