BBC teams and data
 Gety pictures
Gety picturesThe warmer water on the seashore may seem attractive to your vacation, but the last ocean heat wave in the Mediterranean Sea was intense scientists fearing severe consequences for marine life.
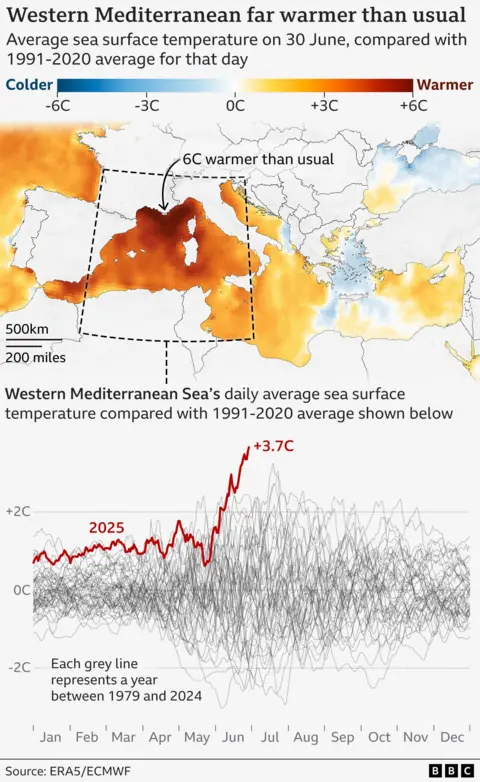
Sea surface temperature passed regularly 30 degrees Celsius off the coast of Majorca and other places in late June and early July, in six or seven degrees above usual.
This may be warmer than the local pool of the entertainment center.
The sea heat wave was absolutely the most extreme in West Meed ever during the time of the year, affecting large areas of the sea for successive weeks.
The heat appears to cool, but some species are struggling to deal with such a long and condensed warmth, with possible effects on fish stocks.
To give you an idea of this temperature, most swimming pools in the entertainment center are heated to approximately 28 ° C. Competitive swimming pools are slightly cooler at 25-28 ° C, as the world says.
Children’s gatherings are somewhat warmer, recommended on 29-31C or 30-32C for children, according to the Swimming Teachers Association.
Quiet temperatures can pose hidden threats. Bacteria and algae are often spreading more easily in the warmer sea water – which are not treated with cleaning chemicals such as a local swimming pool.
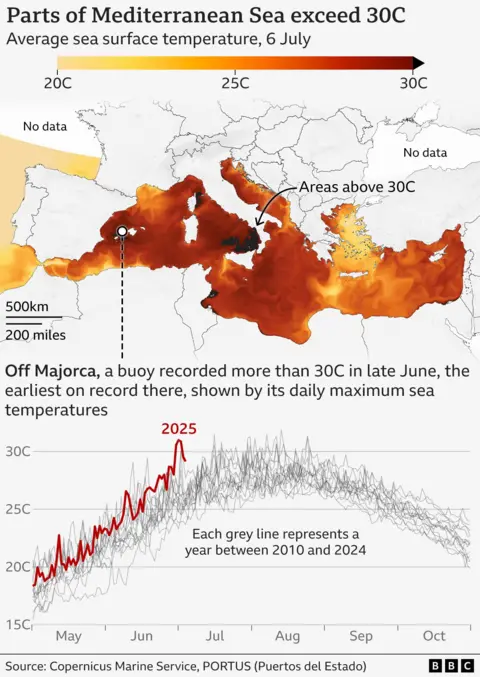
Sea temperatures of 30 degrees Celsius or higher were not preceded in Med in late summer.
But it is very unusual for the month of June, according to data from European climate service from Copernicus, Mercator Ocean International, and the measurements in Spanish ports.
“What is different this year is that 30 degrees of sea temperatures have arrived early, and this means that we can expect the summer to be more dense and longer,” said Marta Marcos, associate professor at the University of Balrick Islands in Spain.
“I grew up here, so we are used to heat waves, but this has become more common and intense.”
“We are all very surprised by the size of this thermal wave,” added Aida Elvira-Esakra, Ocean Photographer at the University of Lij in Belgium.
“It is a matter of great concern, but this is something we can expect to happen again in the future.”
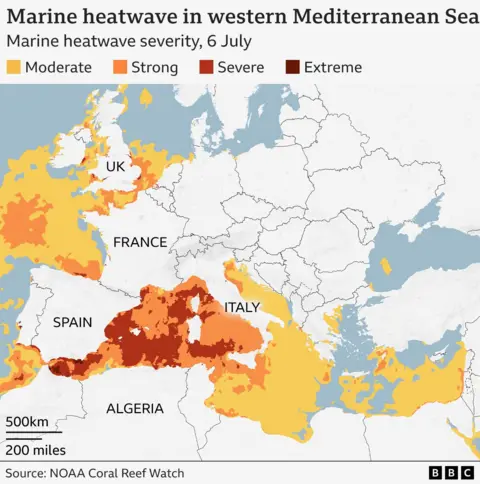
Marine heat waves have become more intense and longer, as humanity continues to release gases that calm the planet in Jonah, mainly by burning coal, oil and gas.
In fact, the number of extremist sea temperature days has doubled over the world over the past eighty years, according to Research published earlier this year.
Dr. Marcus said: “Global warming is the main driver of marine thermal waves … It mainly transfers heat from the atmosphere to the ocean. It is very simple,” said Dr. Marcus.
The Mediterranean Sea is particularly weak because it is somewhat similar to the bathtub, largely surrounded by continents instead of the open ocean.
This means that water cannot escape easily, so its surface rises quickly in the presence of warm air, sunny sky and light winds – As happened in June.
For this reason, MED is a “hot climate change point”, a non -profit research organization, a non -profit research organization.
Its climax reached its climax with the transformation of June to July, after which stronger winds allowed deeper and cooler water to mix it with the warm surface above and temperatures decrease.
But temperatures are still higher than average and there may be consequences for marine life that we do not know yet.
Most of life has a temperature threshold that cannot survive, although it differs greatly between species and individuals.
But marine creatures can also suffer from exposure for a long period of heat, which mainly drains their energy during the summer to the point that they can no longer overcome.
“I remember four years before diving in September at the end of the summer, we found a bone structure for many population,” said Emma Cybian, an environment scientist at the Center for Advanced Studies in Spain.
Sea and seaweed such as the Mediterranean Forests work, home to hundreds of species, as well as carbon dioxide locking that calms the planet.
“Some of them were well adapted to medium medium warm temperatures, but in reality they cannot often carry the conditions of the marine thermal wave, which have become more extremist and deployment.”
 Gety pictures
Gety picturesThe heat can also cause what environmental scientists call “fatal effects without”, as species mainly enter into a survival mode and do not multiply.
“If we start seeing environmental effects, there are certainly effects on human societies (including) fish fisheries losses,” Dan Smil, an older research colleague at the Marine Biological Association in Pleimouth.
“We will have to wait and see, really, but because the temperatures are very high early in the summer, this is really worrying.”
He added that the fast MED is “Canary in the Coal Mine to change climate and marine ecosystems.”
Excessive heat in the oceans can also ship severe weather.
The warmer seas means additional evaporation, adding moisture in the atmosphere that can nourish extreme precipitation.
If the other conditions are correct, this may lead to devastating floods, as happened in Libya in 2023 and Valencia in 2024.
 EPA
EPAThe warmer water can reduce the cooling effect that the coastal population will usually get from the sea breeze.
This can make things very uncomfortable if there is another heat wave later in the summer, as Dr. Marcus warned.
“I’m sure this will be terrible.”

https://ichef.bbci.co.uk/news/1024/branded_news/2a73/live/433762d0-5f24-11f0-960d-e9f1088a89fe.jpg
Source link
