Foy MaxOr Understanding maximum oxygenIt is the widely accepted indicator of Respiratory cardiac tolerance. It represents the body’s ability to connect and use oxygen during continuous physical activity. Vo₂ Max is closely related to sports performance, health results and longevity. However, direct measurement requires expensive equipment and laboratory conditions.
Entered Cooper test-An effective and time -based field method for Vo₂ Max without laboratory equipment.
Hi, I am Alexandra Bothz of FitnessProGRAMERER. I carefully prepared this article to help you understand the 12 -minute operating test Improving Vo₂ Max. And don’t worry, my future articles are designed to keep you engaged, not breathing!
What is the 12 -minute operating test?
the Cooper operation test for 12 minutes It is a simple, but very effective way to evaluate the individual Cardiac resilience and air fitness. The running test includes as much as possible in exactly 12 minutes. Then the total distance that is covered during this time is used to estimate the maximum individual.
It was developed in 1968 Dr. Kennethh. CooperThe former US Air Force doctor, this test was originally designed to evaluate The air ability of military personnel. Practical spontaneity, minimal equipment requirements, and a height of correlation with Foy Max Make it a widely approved tool in both military and civil settings.
Dr. Cooper’s vision was to create a file A simple, evidence -based fitness tool For adult population – after more than 50 years, the test remains a golden standard in endurance assessment around the world.
“This test provides a practical way to estimate the maximum oxygen and physical performance.” – Cooper Kh, Jama, 1968
Cooper’s physiological basis
During the 12 -minute operating test, individuals run with the maximum sustainable pace. this An effort below the maximum to the maximum It reflects:
- Vo₂ max
- Endurance cardiovascular
- Pulmonary heart efficiency
- Near the lactate threshold
- Running economy (to a lesser extent)
The total distance in 12 minutes is Air agent Power system capacityThe longest distances reflect the use of the best oxygen over time. Although it is not the main goal of the test, it also provides an insight into you The ability to speed over timeIt is an essential skill in endurance and race training. Covering more distance in 12 minutes requires a balance between endurance, mental focus and effective energy.
How to perform the operating test for 12 minutes
- Warm up for 5-10 minutes with light jogging and dynamic movement exercises.
- Start the time hour and run continuously for 12 minutes Faster Sustainable pace.
- Stop when you are 12 minutes.
- Measurement or registration Covered accurate distance.
- Calm for 5-10 minutes after testing.
- Use the occasion Cooper Fu, Max format To estimate the air ability.
Cooper Test Performance Categories
If you do not want to calculate Vo₂ Max, you can simply evaluate your cardiovascular fitness based on The total covered distance in 12 minutes. Provides the following table Unified performance classifications For different age and sex groups, based on the original Cooper test and field data that have been validated.
Use the table below:
- I am looking for you The age group and sex.
- Conform it with The distance you achieved During the test.
- Watch your classification – from “poor” to “excellent”.
Cooper Test Categories – Males
| age | excellent | Above average | middle | Lower | poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-19 | more 3000 m | 2700-3000 m | 2500-2699 m | 2300-2499 m | under 2300 m |
| 20-29 | more 2800 m | 2400-2800 m | 2200-2399 m | 1600-2199 m | under 1600 m |
| 30-39 | more 2700 m | 2300-2700 m | 1900-2299 AD | 1500-1899 m | under 1500 m |
| 40-49 | more 2500 m | 2100-2500 m | 1700-2099 m | 1400-1699 m | under 1400 m |
| 50+ | more 2400 m | 2000-2400 m | 1600-1999 AD | 1300-1599 m | under 1300 m |
Cooper Test Categories – Female
| age | excellent | Above average | middle | Lower | poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-20 | more 2300 m | 2100-2300 m | 1800-2099 m | 1700-1799 m | under 1700 m |
| 20-29 | more 2700 m | 2200-2700 m | 1800-2199 m | 1500-1799 m | under 1500 m |
| 30-39 | more 2500 m | 2000-2500 m | 1700-1999 AD | 1400-1699 m | under 1400 m |
| 40-49 | more 2300 m | 1900-2300 m | 1500-1899 m | 1200-1499 m | under 1200 m |
| 50+ | more 2200 m | 1700-200 m | 1400-1699 m | 1100-1399 m | under 1100 m |
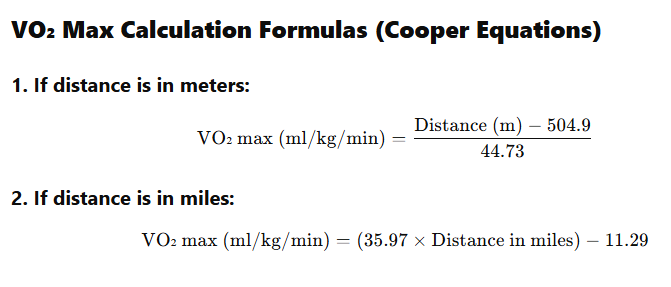
How to calculate Vo₂ Max with a 12 -minute Cooper test
Both formulas provide similar results, so use any system you follow. This is a valuable measure for athletes, fitness lovers and doctors alike.
Cooper Test Calculator
If you prefer not to do mathematics manually, there are many free calculators available on the Internet. Simply enter your distance (meters or miles), and will provide the tool with an accurate estimate of Vo₂ Max.
Standard vocal values by age and sex
men
| age | Sophisticated | excellent | good | justice | poor | Very poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-29 | 66.3 | 59.3-66.2 | 53.7-59.2 | 48.0-53.6 | 41.9-47.9 | 41.8 |
| 30-39 | 59.8 | 54.2-59.7 | 48.0-54.1 | 42.4-47.9 | 37.4-42.3 | 37.3 |
| 40-49 | ≥55.6 | 49.3-55.5 | 43.9-49.2 | 37.8-43.8 | 33.3-37.7 | ≤33.2 |
| 50-59 | ≥50.7 | 43.2-50.6 | 38.2-43.1 | 32.6-38.1 | 28.4-32.5 | 28.3 |
slim
| age | Sophisticated | excellent | good | justice | poor | Very poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-29 | 56.0 | 48.3-55.9 | 43.2-48.2 | 37.6-43.1 | 32.0-37.5 | 31.9 |
| 30-39 | 45.8 | 39.3-45.7 | 34.6-39.2 | 30.2-34.5 | 26.4-30.1 | 26.3 |
| 40-49 | 41.7 | 36.0-41.6 | 31.1-35.9 | 26.7-31.0 | 23.3-26.6 | ≤23.2 |
| 50-59 | 35.9 | 30.2-35.8 | 26.8-30.1 | 23.4-26.7 | 20.6-23.3 | ≤20.5 |
The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM). ACSM instructions for testing exercise and prescription, tenth version, 2017.
Benefits of Cooper Test
- It has been scientifically validated: High connection with the direct Vo₂ Max test
- Low cost: No specialized laboratory or equipment requires
- Effective: A 12 -minute test, can be repeated easily
- Various abilitiesIt applies to individuals, teams, schools and army
- Follow progressIdeal to monitor training adaptations over time
Cooper test restrictions
- It requires maximum effort for accuracy
- Environmental factors (weather, wind and height) may affect the results
- The running economy may tend to the results of high or non -trained individuals
- Less convenient for the elderly or those who have joint restrictions/mobility
- It is not useful for those who cannot run or suffer from muscle injuries
The effects of training
Vo₂ max is training. normal Air training-especially High -density separation training (Welcome))and timeAnd Long stable heart disease– Vo₂ max can be increased 15-25 % In most people.
The Cooper Test can be used 6-12 weeks To assess the effectiveness of training.
Who should use a Cooper test?
- Athletes: To track the basis and track progress
- Coaches and coaches: To evaluate the team or customer for fitness and blood vessels
- Military, fire, law enforcementAs part of the rehabilitation of fitness
- The general population: To monitor health and wellness
Cooper’s test alternatives
| Test name | Best for | It requires equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Walking test is one mile from Rubport | Beginners/the elderly | Timing watch |
| Multi -stage bile test | The difference/athletes | CD/App, cones |
| Bruce Mill | Clinical settings and laboratory | Walking device and laboratory |
conclusion
the Cooper for 12 minutes It is still one of the most common, simple and effective ways to estimate Vo₂ Max. It blocks the gap between science and ease-while giving any athletes to individuals who realize health follow the performance of the heart and blood vessels.
Whether you are preparing for a race, a training plan, or improve your health standards, the Cooper test provides a A reliable snapshot of your air fitness.
Scientific references
- Cooper K. (1968). A way to assess the maximum amount of oxygen: the relationship between the field and the mill test. mosque. 203 (3), 201-204. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1968.03140030033008
- BIOL SPORT 2014. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Arttingles/pmc4314605/
- Grant, S. And others. (1995). A comparison between the prediction methods of maximum absorption of oxygen. Br J Sports Med, 29 (3), 147-152.
- Noonan, V., & Dean, E. (2000). Exercise test under the maximum: clinical application and interpretation. Physiotherapy, 80 (8), 782-807.
- Bassett, DR, & Howley, ET (2000). Factors to reduce the maximum oxygen absorption and endurance determinants. Med Sci SPORTS exercises, 32 (1), 70-84.
https://fitnessprogramer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/12-Minute-Run-Test.webp
Source link